Cocaine is an addictive stimulant drug that can be injected, snorted, smoked, or used orally. Although it is used in some medical settings as an anesthetic, it is illegal for recreational use in the United States.
Drug screenings can be ordered as a preventative measure or as a result of someone showing signs or symptoms of drug abuse. Blood testing is commonly used to monitor prescription drug use and to test for the use of illicit drugs like cocaine.
Cocaine Detection Time In Blood
The detection time for cocaine refers to the length of time cocaine use can show up in a drug test. Different drug testing methods have cutoffs for how much of a drug or its metabolites must show up in a screening to indicate drug use.
Cocaine can be detected in blood samples for up to 24 hours, or one day, after your last use. This is an average estimate. The actual detection window can vary based on a number of biological, genetic, and personal factors related to your drug use.
How Do Drug Tests Detect Cocaine Use?
Cocaine has a short half-life, which means it is metabolized in the body very quickly. Cocaine is metabolized by enzymes in the blood and liver.
Drug screens for cocaine generally screen for benzoylecgonine, the main metabolite of cocaine.
Cocaine metabolites can be detected in:
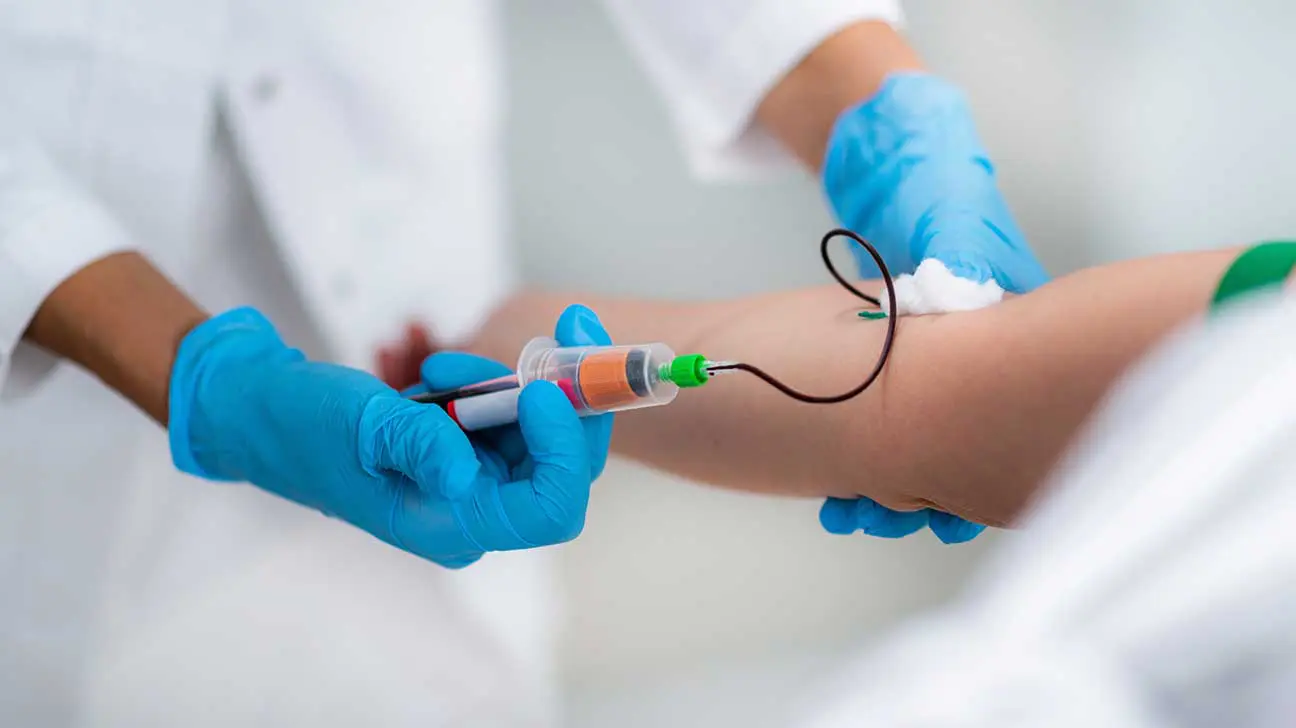
Blood testing is conducted in a hospital or laboratory setting. During the test, a healthcare professional will take a sample of blood by inserting a syringe into the arm. This will allow the tube attached to the needle to fill with blood, which can then be tested for cocaine metabolites.
What Can Affect Drug Detection Times?
Cocaine detection times are not the same for everyone. A variety of biological, genetic, and personal factors related to drug use can shorten or lengthen the drug detection time frame.
Factors that can affect drug detection times:
- how much cocaine is used
- route of administration (e.g. snorting, smoking, injecting)
- how often cocaine is used
- history of drug use
- history of mental illness
- polydrug/polysubstance abuse
- body composition (e.g. weight, body fat, height)
- genetics
- age
How long cocaine stays detectable in the system can also depend on whether you’ve used cocaine once, or have used it over a long period of time. Chronic cocaine use and addiction can alter the metabolism of the drug in the body.
Why Are Blood Tests Used?
Blood tests for drug use are commonly used to monitor the use of prescription drugs like opioids, which can be abused and become addictive when taken in ways other than prescribed.
Drug screens can be used for many reasons, including:
- pre-employment screenings
- recurring workplace drug testing
- criminal investigations
- court-mandated drug testing
- professional athlete drug testing
- suspected illicit drug use
Urine tests are the most common method for detecting drugs like cocaine. However, a healthcare provider may order a blood test if they notice a patient demonstrating common signs or symptoms of illicit substance use.
Signs And Side Effects Of Cocaine Use
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that can increase your heart rate, boost energy, and produce a sensation of pleasure within seconds to minutes after use.
Signs of cocaine abuse can include:
- chronic runny nose
- track marks (from injection)
- tooth decay
- dramatic weight loss
- mood swings
- psychosis (hallucinations, delusions, paranoia)
- poor judgment
- memory problems
- fast or irregular heartbeat
- muscle twitches
- irritability and aggression
- lack of empathy
The short-term side effects of cocaine can wear off within minutes. This often leads to cocaine binges, whereby someone will take additional doses of cocaine for hours or days on end before crashing.
Cocaine is highly addictive and can cause a range of short-term and long-term consequences to health, employment status, relationships, and psychological well-being.
If you’re concerned about cocaine showing up in a blood test, it may be time to consider seeking professional treatment.
Finding Treatment For Cocaine Abuse And Addiction
Thousands of people begin rehab programs for cocaine addiction each year. If you or a loved one are addicted to cocaine: You’re not alone. Recovery is possible.
Call our helpline today to learn more about different treatment options for cocaine addiction and how to find an addiction treatment center near you.
Addiction Resource aims to provide only the most current, accurate information in regards to addiction and addiction treatment, which means we only reference the most credible sources available.
These include peer-reviewed journals, government entities and academic institutions, and leaders in addiction healthcare and advocacy. Learn more about how we safeguard our content by viewing our editorial policy.
- U.S. Department of Energy: Office of Health, Safety, and Security—Drug Detection Study
https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/908420 - U.S. National Library of Medicine: MedlinePlus—Drug Testing
https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/drug-testing/ - National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)—Drug Testing
https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/drug-testing - National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)—Cocaine DrugFacts
https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/cocaine


